The Importance of Collagen for Skin Health:
How to Include It in Your Routine

The Importance of Collagen for Skin Health Collagen is a vital protein that plays a fundamental role in maintaining skin elasticity, hydration, and overall health. As we age, collagen production naturally declines, leading to visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles, sagging, and dryness. However, by incorporating the right foods, supplements, and skincare techniques, you can slow down collagen loss and promote a youthful complexion.
This article explores the science behind collagen, the best ways to boost its production, and how to incorporate it into your daily routine for optimal skin health.
What Is Collagen and Why Is It Important?
Collagen is the most abundant structural protein in the human body, accounting for nearly 75% of the skin’s dry weight. It forms a fibrous network in the dermis, providing strength, elasticity, and hydration. In addition to its role in skin health, collagen is a critical component of connective tissues, including tendons, ligaments, and bones. Research published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology highlights that collagen supplementation can significantly improve skin elasticity, hydration, and overall texture after just eight weeks of consistent use.
The Aging Process and Collagen Loss
Starting in our mid-20s, collagen production decreases by approximately 1% per year. By the time we reach our 40s and 50s, the effects become more visible, leading to:
- Wrinkles and fine lines
- Loss of skin firmness
- Increased dryness
- Slower wound healing
Factors That Accelerate Collagen Depletion
The degradation of collagen is not just a natural part of aging; it is also heavily influenced by lifestyle and environmental factors. Sun exposure, poor diet, smoking, and stress, for example, can accelerate this process, compromising skin and joint health.
Excessive UV exposure is one of the leading causes of collagen damage, as it triggers an overproduction of enzymes called matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which degrade collagen fibers and accelerate wrinkle formation. A diet high in processed sugars and refined carbs can lead to glycation, a process where sugar molecules bind to collagen, making it rigid and prone to breakage. Additionally, smoking introduces over 4,000 toxins into the body, many of which generate free radicals that degrade collagen. Even chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, disrupting collagen synthesis and weakening skin structure. To counteract these effects, adopting an antioxidant-rich diet, wearing sunscreen daily, and managing stress are essential steps in maintaining youthful, firm skin.
Several external factors can speed up collagen breakdown, including:
- Excessive sun exposure – UV rays damage collagen fibers, leading to premature aging.
- Poor diet – High sugar intake accelerates glycation, which weakens collagen structure.
- Smoking and pollution – Oxidative stress damages collagen and slows its production.
- Chronic stress – Elevated cortisol levels contribute to collagen degradation.
- Lack of sleep – Poor rest inhibits the body’s ability to repair and regenerate skin.
Types of Collagen and Their Benefits
There are 28 different types of collagen, each serving a specific function in the body. These types are found in various tissues, including the skin, bones, tendons, and cartilage, providing strength, flexibility, and structural support. However, when it comes to skin health, elasticity, and hydration, the most important types are:
Type I Collagen – The Foundation of Youth
- Makes up 80-90% of the skin’s collagen
- Essential for firmness, elasticity, and wrinkle prevention
- Also supports bones, tendons, and ligaments
Type I collagen is the most abundant and structurally important collagen for youthful skin. It acts as a scaffold, providing strength and resistance to sagging. Studies show that hydrolyzed Type I collagen peptides can increase skin hydration and elasticity by significantly reducing wrinkle depth in as little as 8 weeks.
Type III Collagen – The Hydration Booster
- Works alongside Type I to maintain skin smoothness
- Enhances hydration and skin barrier function
- Important for blood vessels, muscles, and organ health
Type III collagen is often found in younger skin, but its production declines with age. This type is particularly abundant in connective tissues, contributing to plumper, more resilient skin. Many collagen supplements combine Type I and III for maximum anti-aging benefits.
Type IV Collagen – The Skin Regenerator
- Forms the basement membrane, essential for cell renewal
- Strengthens the skin’s protective barrier
- Supports wound healing and overall skin regeneration
Unlike Types I and III, which provide structure, Type IV collagen acts as a filtration layer, helping the skin repair itself and maintain hydration. It plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation and keeping the skin smooth and resilient against external stressors like pollution and UV damage.
Which Type of Collagen Is Best for Skin?
For maximum skin benefits, look for supplements containing hydrolyzed Type I and III collagen peptides, often combined with Vitamin C and hyaluronic acid to enhance absorption and boost hydration.

How to Boost Collagen Naturally
While collagen production naturally declines with age, you can take proactive steps to stimulate its synthesis and maintain firm, hydrated, and youthful skin. The best strategies combine nutrition, supplementation, skincare, and lifestyle changes to protect and enhance your body’s collagen levels.
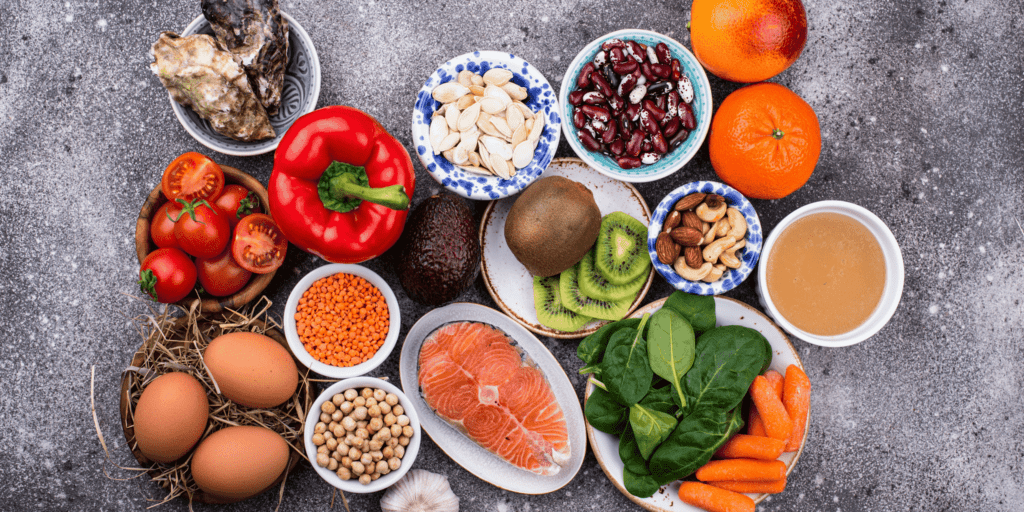
Eat Collagen-Boosting Foods
Your diet plays a fundamental role in collagen synthesis. Certain foods provide the building blocks (amino acids) and cofactors (vitamins & minerals) necessary to stimulate production.
Food | Collagen-Boosting Benefits |
Bone broth | Naturally rich in collagen, gelatin, and amino acids |
Salmon & Fatty Fish | Omega-3 fatty acids help protect collagen from breakdown |
Egg whites | Contain proline, a key amino acid for collagen formation |
Citrus fruits | High in vitamin C, an essential cofactor for collagen synthesis |
Leafy greens (spinach, kale) | Rich in antioxidants that protect collagen from oxidative stress |
Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) | Packed with polyphenols that enhance collagen stability |
Pro Tip: Pair vitamin C with collagen-rich foods! Without vitamin C, your body cannot efficiently produce or maintain collagen levels.
Take High-Quality Collagen Supplements
Supplements containing collagen have received scientific support for their skin-rejuvenating benefits. Studies suggest that they can help improve skin elasticity, hydration, and reduce wrinkles, making them a popular choice for those looking to maintain a youthful appearance. Studies show that hydrolyzed collagen peptides can increase skin hydration, elasticity, and reduce wrinkle depth within 8 to 12 weeks.
What to Look for in a Collagen Supplement:
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides – Easily absorbed for maximum effectiveness
Type I & III collagen – Best for skin elasticity and hydration
Vitamin C – Enhances collagen synthesis
Hyaluronic acid – Retains moisture and improves skin plumpness
Antioxidants (e.g., CoQ10, polyphenols) – Protect collagen from free radical damage
Best Supplement Forms:
- Powdered collagen – Mixes easily into smoothies, coffee, or water
- Collagen capsules – Convenient for daily intake
- Collagen drinks – Ready-to-drink options with added vitamins
Use Skincare Products That Stimulate Collagen
Certain topical ingredients have been proven to enhance collagen production and protect against degradation:
- Retinol (Vitamin A) – Increases cell turnover and stimulates collagen synthesis
- Vitamin C Serums – Protects existing collagen and boosts new production
- Peptides – Signal skin cells to produce more collagen
- Hyaluronic Acid – Keeps skin hydrated, preventing collagen loss
Expert Tip: Always apply sunscreen (SPF 30+) daily—UV exposure is the #1 cause of collagen breakdown!
- Adopt a Collagen-Friendly Lifestyle
Your daily habits play a significant role in preserving collagen and maintaining youthful skin.
Get 7-9 hours of sleep – Sleep is when your body repairs and regenerates collagen
Exercise regularly – Improves blood circulation and stimulates collagen production
Reduce sugar intake – Excess sugar leads to glycation, which weakens collagen fibers
Stay hydrated – Dehydrated skin is more prone to collagen degradation
Avoid These Collagen Killers:
- Excessive sun exposure (UV rays break down collagen)
- Smoking (reduces oxygen flow to skin cells)
- High sugar consumption (damages collagen structure)
Final Thoughts: Can You Really Boost Collagen Naturally?
Absolutely! By combining a collagen-rich diet, scientifically-backed supplements, effective skincare, and healthy lifestyle habits, you can slow collagen loss, improve skin texture, and achieve a radiant, youthful glow.
Sources:
- Proksch, E., Segger, D., Degwert, J., Schunck, M., Zague, V., & Oesser, S. (2014). “Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study.” Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
• Bolke, L., Schlippe, G., Gerß, J., & Voss, W. (2019). “A collagen supplement improves skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles: A randomized, placebo-controlled study.” Nutrients.
• Zague, V. (2008). “A new view concerning the effects of collagen hydrolysate intake on skin properties.” Archives of Dermatological Research.
• Healthline – Collagen for Skin: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/collagen-for-skin
• WebMD – Collagen: Benefits and Uses: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1301/collagen
• Mayo Clinic – Collagen Supplements: https://www.mayoclinic.org/collagen-supplements